21, Aug. 2019
News
The subject of fintech has been making headlines for several years now, with global funding to the sector rising 120 percent in the space of a year to reach US $111.8 billion in 2018. The definition of fintech is the harnessing of technology to improve financial services and to date the most widely known example is its usage in digital payments via smartphone or the internet. Fintech’s application and potential are huge and wide-ranging though, and its disruption of traditional banking has made banks sit up and take notice. The future of fintech and of banking lies, however, not in any form of competition between the two but in a collaborative approach. By working together, the strengths of each can thus be leveraged: banks bring with them a large client base, an established bond of trust with their clientele, robust brand equity, and greater knowledge of regulatory compliance while fintech offers innovation, agility to change and a consumer-centric approach.
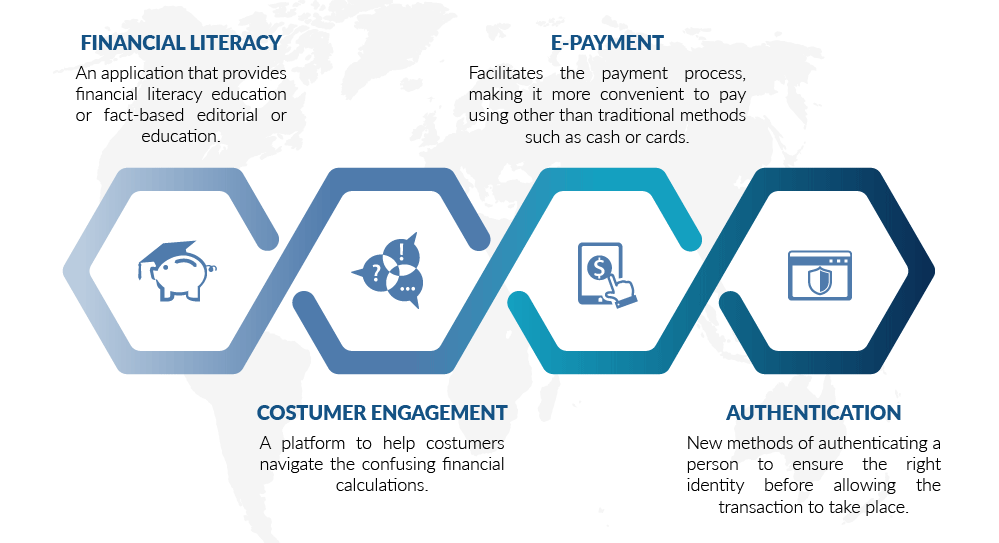
In the domain of private banking, fintech’s impact is currently on the rise, and the momentum is growing. What makes fintech’s incorporation into private banking interesting is that this sector has traditionally relied on the personal touch in its interactions with customers, who are predominantly ultra high net worth individuals (UHNWI) and high net worth individuals (HNWI). However, the younger, more tech-savvy of these upper tier clients are more inclined to want instant access and solutions that digital platforms offer. Certainly, in private banking, the human touch can never be entirely replaced though. Some customers still prefer personal interaction to digital interfaces regardless. FFA Private Bank’s powerful online trading platform is one example of this, as despite offering trading at a more financially beneficial rate, many customers still prefer off-line trading at a higher cost.
Fintech offers possible advantages to private banking in a number of key areas. One is its ability to provide customer insight and advanced analytics. Artificial intelligence (AI) can be used to improve the screening process of potential clients as well as to make the onboarding process, traditionally involving lengthy requirements, more efficient and accurate. With digital capabilities at their fingertips, and routine tasks automated, wealth managers would then find themselves free to concentrate on value-added activities and improving the customer experience, which after all is what distinguishes private banks from its other banking peers.